DO-178B and DO-178C Standards
The Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification standard, also known as RTCA DO-178B is a software certification standard that is used for airborne systems. And as expected, such systems require the safety of the software. Simply, DO178B is a guideline that is used for this purpose. The standards are published by the Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics (RTCA) with the combined work of the European Organisation for Civil Aviation Equipment (EUROCAE) as DO-178B in 1992 and as DO-178C in 2011. They are nearly identical, nevertheless the latter is just a revised version. Since the standards are identical in content, they will be referenced as DO-178 from now on in this article. The standards are known as DO-178B in the US due to RTCA and ED-12B in Europe due to EUROCAE. Both organizations accept each other’s certificates.
DO-178 standards provide higher reliability and stability, reusability, lower life cycle cost, lower maintenance cost, and faster software compatibility.
According to the DO-178 guidelines, all airborne software must be assigned a Design Assurance Level (DAL) based on the consequences of a system failure. The lowest level is E, which means “no safety effect” and the highest is A, which means “catastrophic.” The standards define a variety of process goals that differ depending on the software level.
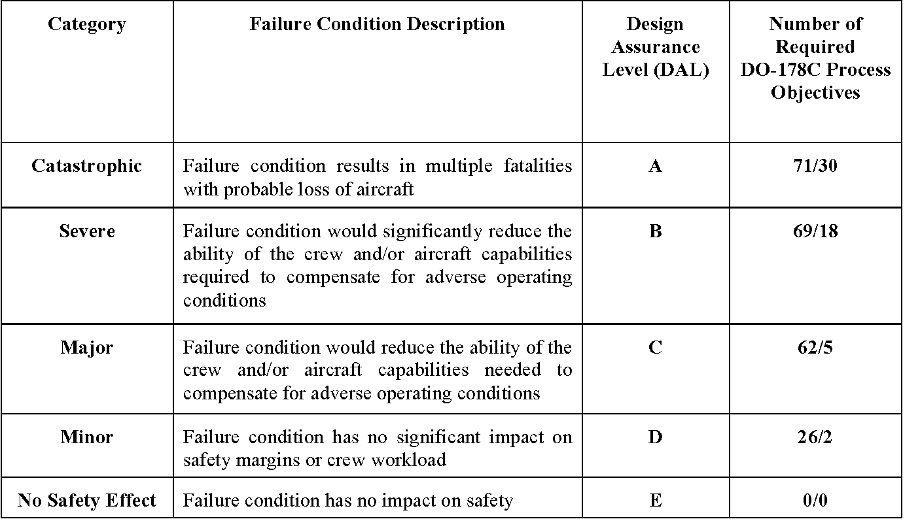
Obviously, the higher criticality levels require more objectives to be fulfilled. Nonetheless, it should be noted that DO-178, by itself, doesn’t guarantee the safety of the system. Additional necessary system safety duties must be assigned to safety characteristics in the design and implemented as functionality in order to provide and achieve objective proof of attaining desired safety criteria. Also, it is worth mentioning that the assigned criticality level depends on the aircraft type.
After the determination of the DAL level planning process and development process should be carried out respectively. And throughout these processes, a correctness process should be performed in parallel.
As part of the planning process the following plans must be produced as part of this activity:
- Plan for Software Aspects of Certification (PSAC)
- Software Development Plan (SDP)
- Software Verification Plan (SVP)
- Software Configuration Management Plan (SCMP)
- Software Quality Assurance Plan (SQAP)
In addition to that, the development process consists of all activities related to the design and production of DO-178 software that fulfills the project’s system requirements. This comprises defining high and low-level software requirements, as well as software design and implementation.
Finally, at the end of the verification process, verification steps that are planned in the planning process should be conducted accordingly. As a result, necessary proof should be generated and demonstrated to certification authorities such as Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). These organizations supervise all areas of civil aviation both within their country and across international waterways.








 Mor Teknoloji
Mor Teknoloji






